Quick Facts
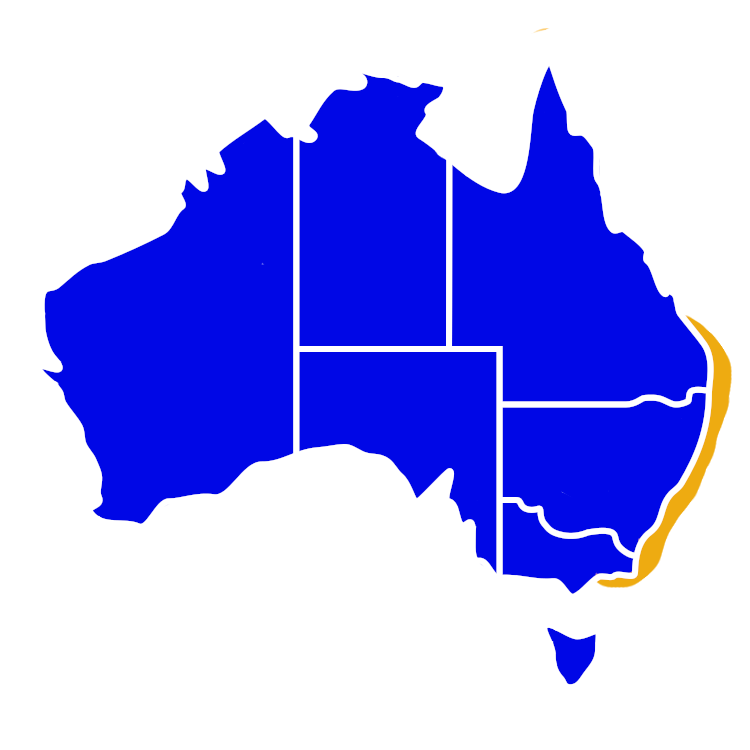
Distribution
Interesting Info
- The Trumpeter Whiting is a medium-sized whiting found on the east coast of Australia, from southern Queensland to southern New South Wales, with occasional records further south into eastern Victoria.
- Its common name comes from the croaking or grunting sound it produces when caught, made by vibrating muscles against the swim bladder.
- The body is pale silver to grey with distinctive dark blotches or bars scattered along the flanks, which help identify it from Sand and Goldenline Whiting.
- Juveniles inhabit shallow sandy estuaries, tidal flats, and seagrass beds, while adults move to deeper estuarine channels and coastal sandbanks.
- They are schooling fish, often forming dense aggregations over sandy bottoms, which makes them a common catch for both recreational and commercial fishers.
- They feed on benthic invertebrates such as worms, amphipods, small crabs, shrimps, and molluscs, using a protrusible jaw to suck prey from sand.
- Spawning occurs offshore in warmer months, with eggs and larvae drifting back into estuaries where juveniles develop.
- Their lifespan is around 6–7 years, with most fish caught between 2–4 years of age.
- Predators include flathead, mulloway, tailor, trevally, and seabirds, particularly in shallow estuaries and surf gutters.
- They are a popular recreational target, caught from beaches, estuary mouths, and piers using baits like worms, yabbies, and pipis.
- Commercially, they are taken in estuarine and inshore net fisheries, marketed fresh and used in the fish-and-chip trade.
- Their ecological role includes regulating invertebrate populations on sandy flats and serving as prey for larger estuarine and coastal predators.
Species Interaction
Recreational Fishing, Snorkeling & Diving
Trumpeter Whiting are a popular target for recreational fishing due to their abundance, availability, and good eating qualities. They are often sought after by anglers using light tackle and bait such as beach worms or small pieces of shrimp. In the wild, they can be observed by snorkelers and divers, they exhibit interesting behaviours such as pursuit feeding, where they probe the sand or mud to hunt for prey. Watching their feeding techniques and schooling behaviour can be captivating.
Scientific Classification
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Actinopterygii
Order: Perciformes
Family: Sillaginidae
Genus: Sillago
Species: Sillago Maculata
Conservation Status
In terms of conservation status, the Trumpeter Whiting is not listed as a threatened species in Australia. However, it is still important to manage their populations sustainably to ensure their long-term survival.
Fish Taste Quality
Trumpeter Whiting are highly regarded as a good table fish due to their firm, white flesh and delicate flavour. They have a mild and sweet taste that is often compared to other popular white-fleshed fish species.
Taste Rating: 4/5
How to catch
Trumpeter Whiting
Catch Difficulty: Easy
Tackle: Patternoster Rig, Running Sinker Rig, Artificial Rig
Bait: Crab, Fresh cut flesh baits, Lures, Pilchards, Prawns, Shellfish, Squid, Worms, Yabbies, Soft plastics
Technique: Keep bait on the bottom, Cast bait/jig/lure near schooling fish
Popularity: Highly targeted
Recreational Viewing
- Snorkeling & Scuba
Finding: Easy
Temperament: Peaceful
Location: Inner Reef, Lagoon, Seagrass Beds, Sandflats
Danger: None





